Microsoft has releases its latest iteration of
Dynamics 365 – Spring 2018. I had previously written about, What's new in Sales
and Customer Service. This blog focuses on an updated / new feature –
Knowledge Management. I am sure this will be a useful tool for all businesses to
build a knowledge management strategy. As employees transition, the
knowledge repository should stay and grow as an organizational asset.
Knowledge management allows to create, search, edit, review,
translate and publish knowledge articles. Knowledge articles can be any
customer issues, F.A.Q’s, new business process training, how to steps that a
user can search for and get benefited. Knowledge articles can include
images and videos.
Use Cases for Knowledge Management –
1.
Customer Service Management - Knowledge Management
is crucial for customer service / call center operations. It allows to store
the steps / process for troubleshooting / resolving an issue and make it
available for all users. The customer service agents can also email the
knowledge article to the customer.
2.
Training – Knowledge Management can also be used
for internal training. For example – there is a new sales process implemented,
the Sales Manager can define the process steps in the knowledge management
article and make it available on the sales entity like Opportunity or Lead. Now
any Sales user can than search and refer to the knowledge article to better
understand the new Sales process. Another useful feature for training is the
Learning Path.
3.
In-house back-office support / IT support –
In-house IT routine support calls can by minimized by providing detail
troubleshooting steps to end users. So when a user searches for a particular
issue like - how to reset password, the knowledge article can provide the
answers.
Knowledge Management security and business process –
The knowledge management process can be managed by a user / team.
There is a custom security role called Knowledge Manager created OOTB with full
access to Knowledge article entity. Customer service manager and rep role users
OOTB security role have the read and create capability for knowledge article.
Any other users who need access to the knowledge articles (my guess is all
users) should have at least read access to the knowledge articles entity.
The business process for knowledge article is shown below –
 |
| Knowledge article process |
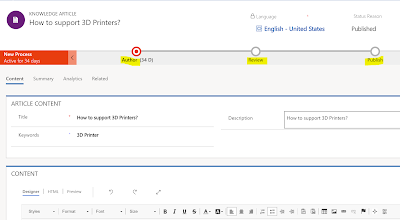
The business process flow for Knowledge article in Dynamics
365 is shown below. There are 3 stages – Author, Review and Publish.
 |
| Business process flow |
The business process stages and steps are detailed below –
1.
Author –
a.
User creates a knowledge article. The article
status reason is proposed.
b.
Once created the knowledge article is given a
major version 1 and minor version 0.
c.
User completes the article and marks it for
review.
d.
This changes the status to in review and the bpf
is moved to the next stage. Also the knowledge article can be manually assigned
/ sent to the Reviewer user or to Reviewer team queue (Automating this process
is recommended)
 |
| Author stage |
2. Review –
The reviewer who is assigned the article can
now pick the article and reviews it. If it needs modifications they can reject
the article and add a reason. If they are ok with the article they can approve
the same.
 |
| Review stage |
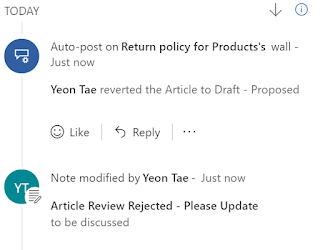
If the article is rejected, the reject reason gets
posted in the timeline of the article and it gets assigned back to the user who
created the article.
 |
| Reject reason post |
There is also an additional “Update Content” stage
added to the knowledge article.
 |
| Update Stage added |
The author of the article can complete the update as
needed and assign it back to the reviewer user or team for finalizing and publishing
the article.
3. Publish
If everything is correct, the reviewer add product
associations and can also add an expiry date.
 |
| Publish stage |
Once complete the article is ready to be published.
The manager can publish the article now or on a future scheduled date. Also set
the expiry date and status of the article after it expires as shown below.
 |
| Publish article |
In addition to above the following
functionality is also available
1.
Article translation into multiple languages
2.
Article views / analytics
3.
Article linked to records like Case
4.
Article versioning capability
Hope this helps in getting started with and
implementing a knowledge management strategy. Thanks for reading.
Mihir Shah
365WithoutCode